Friday Facts is a new series in which we present a data point or bit of information from the latest set (2023) of Report Cards on Child and Youth Sex Trafficking. On every Friday this year, we will feature a fact from one state (or Washington, D.C.). During the course of 2024, we will walk through, in random order, all states plus the nation’s capital.
Facts for Idaho:
- Overall grade: F (in the bottom tier of all states)
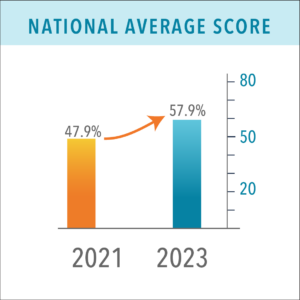
- Between 2021-2023, the state raised its score by 5.5 points (on a 100-point scale).
- In the state, both traffickers and buyers of sex with children can be prosecuted under commercial sexual exploitation offenses.
See more about Idaho’s grade on Shared Hope’s Report Cards on Child and Youth Sex Trafficking.